Pathogenic Yeasts (Candida and Cryptococcus)
Two genera of yeasts stand out as human pathogens, one being Cryptococcus sp. and the other Candida sp.
Cryptococcosis, caused by yeast Cryptococcus neoformans invading tissues when immunity weakens, which could lead to fungal meningitis. Yeast Cryptococcus neoformans usually associates with bird dropping from pigeons. The potential danger is that the sexual spores of this yeast could be carried by wind.
Cryptococcosis, caused by yeast Cryptococcus neoformans invading tissues when immunity weakens, which could lead to fungal meningitis. Yeast Cryptococcus neoformans usually associates with bird dropping from pigeons. The potential danger is that the sexual spores of this yeast could be carried by wind.
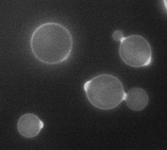
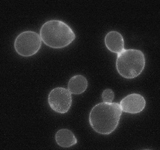
Cryptococcus neoformans 1000x stained with Calcofluor. (C) BioIdea
Candidiasis, caused by Candida albicans, or lesser by C. tropicalis and C. glabrata. The species is commonly present in human mucosa, which becomes invasive when immunity weakens. In newborns natural resistance is low, candidiasis can develop within a few days. Disseminated Cadidiasis can be fatal when untreated.
Candidiasis, caused by Candida albicans, or lesser by C. tropicalis and C. glabrata. The species is commonly present in human mucosa, which becomes invasive when immunity weakens. In newborns natural resistance is low, candidiasis can develop within a few days. Disseminated Cadidiasis can be fatal when untreated.
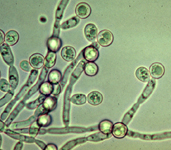
Candida albicans, showing pseudohyphae with clamydospores, this fungus usually takes yeast form. Courtesy of drfungus.org.
